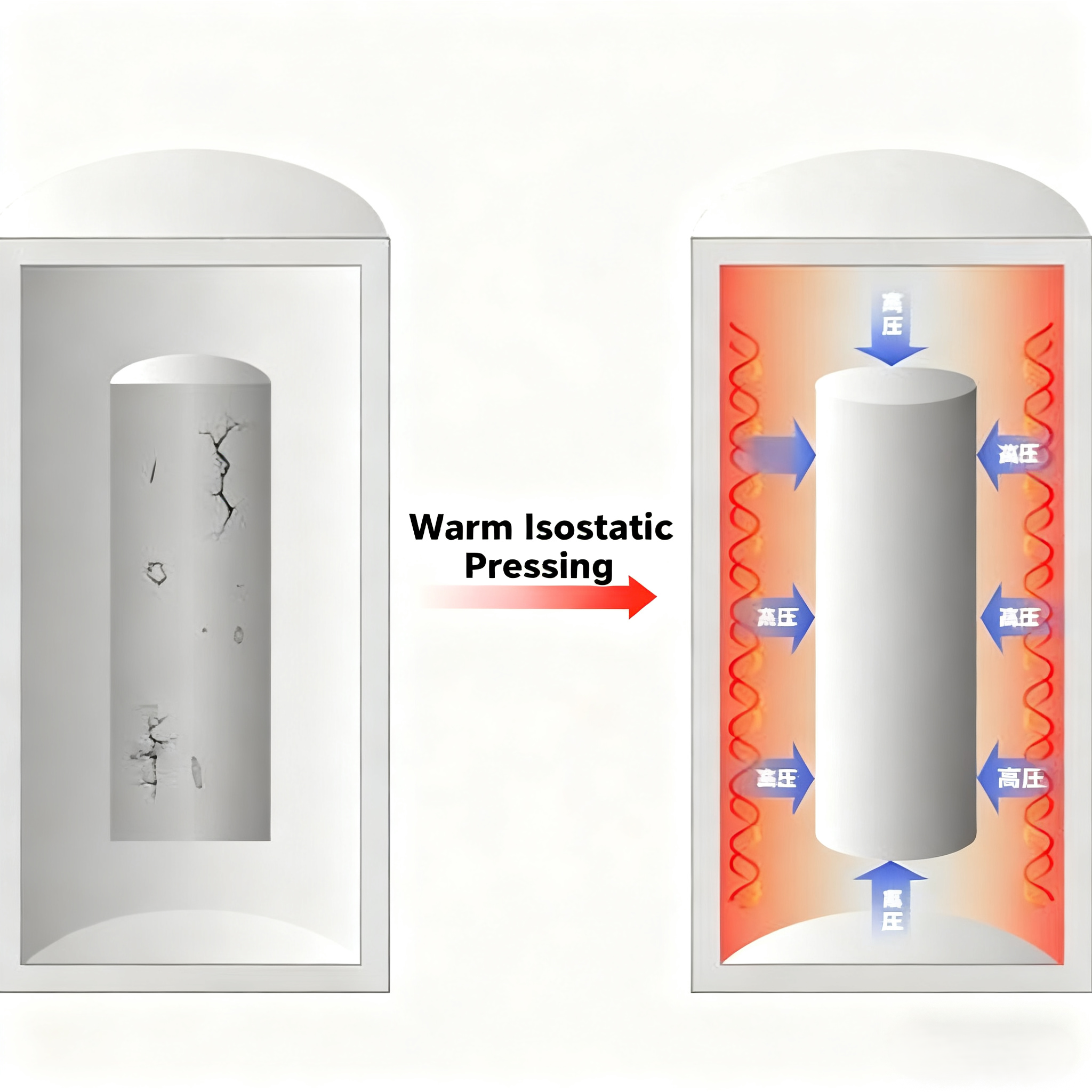
What is Warm Isostatic Pressing (WIP)?
Warm isostatic pressing uses flexible materials as molds, and depending on the material being processed, the pressurizing medium can be water or oil, to shape and press powdered materials. In this process, the liquid is first heated and then injected into a sealed, high-pressure chamber through a pressure source. The pressure of the medium within the sealed container can be uniformly transmitted in all directions, ultimately resulting in products with uniform density and excellent performance. Due to its unique forming advantages, warm isostatic pressing has been widely used in many high-end industrial fields.
New Material Preparation: Forming of blanks for high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys, ceramic matrix composites, and superhard materials (such as silicon nitride and alumina) to provide high-performance substrates for aerospace and nuclear energy fields.
Electronics and Ceramics: Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC), LTCC/HTCC packaging substrates, high-voltage electromagnetic ceramic insulators, etc., ensuring consistent electrical performance and dimensional accuracy.
Special Material Processing: Densification treatment of graphite electrodes, polyamide products, rare earth permanent magnets, and rare metal powders to improve material strength and conductivity.
Precision Manufacturing: Automotive engine turbine blades, medical implants (such as ceramic prostheses), cutting tools, etc., meeting the reliability and service life requirements of high-end equipment.
New Material Preparation: Forming of blanks for high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys, ceramic matrix composites, and superhard materials (such as silicon nitride and alumina) to provide high-performance substrates for aerospace and nuclear energy fields.
Electronics and Ceramics: Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC), LTCC/HTCC packaging substrates, high-voltage electromagnetic ceramic insulators, etc., ensuring consistent electrical performance and dimensional accuracy.
Special Material Processing: Densification treatment of graphite electrodes, polyamide products, rare earth permanent magnets, and rare metal powders to improve material strength and conductivity.
Precision Manufacturing: Automotive engine turbine blades, medical implants (such as ceramic prostheses), cutting tools, etc., meeting the reliability and service life requirements of high-end equipment.
What are the advantages of Warm Isostatic Pressing?
-
Increased DensityUniform heat facilitates material compaction to eliminate porosity, thereby increasing the material's density.
-
Specialized ApplicationsIt is an ideal technology for materials that cannot withstand high temperatures, such as hot isostatic pressing.
-
Lower ConsumptionIt is more economical because it requires a lower temperature than hot isostatic pressing.
-
Mechanical PropertiesImproved mechanical properties make the material more durable and long-lasting.
Equipment product characteristic parameters
| Basic Parameters | Parameter Values |
| Equipment Specifications | Diameter: 380mm; Effective Volume: 600L |
| Operating Temperature | <180℃; Customizable |
| Pressure Increase Time | ≥180 seconds; adjustable |
| Pressure Holding Time | Adjustable |
| Pressure Increase Curve | Adjustable |
Application Areas of Warm Isostatic Pressing Technology
-
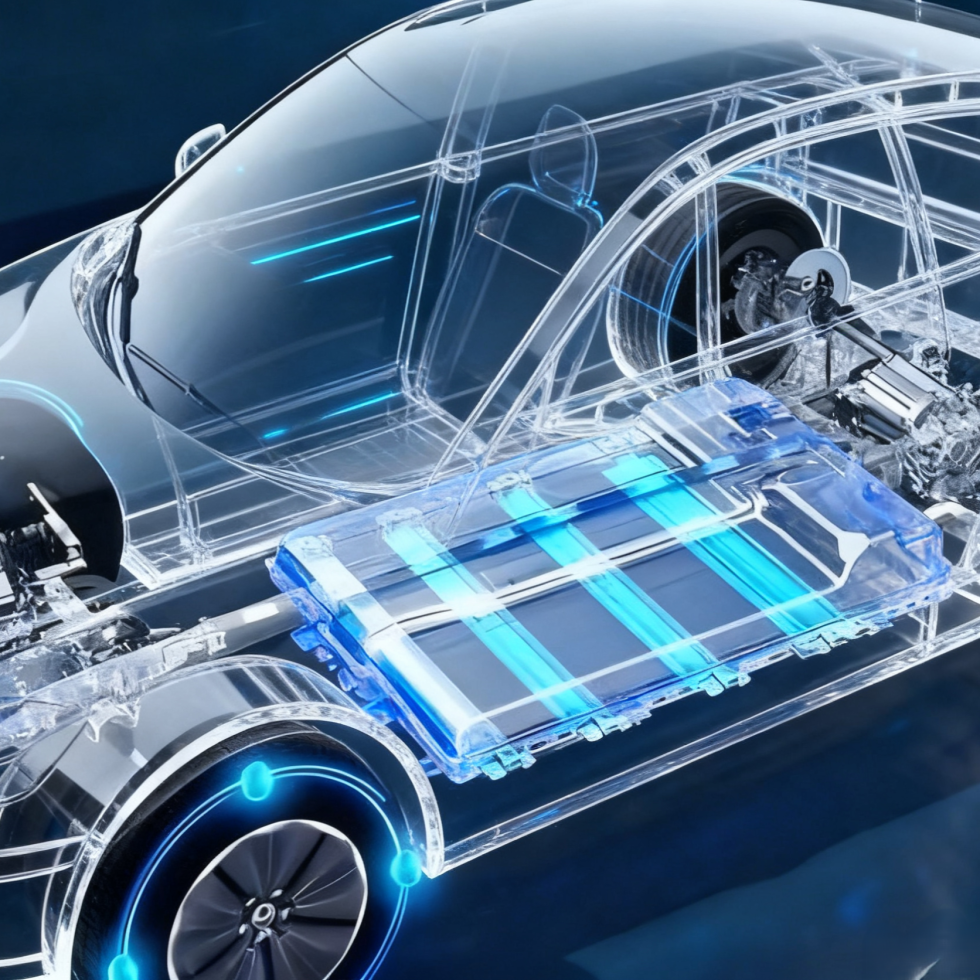 01It is used to improve the interfacial density between solid electrodes and electrolytes in solid-state batteries, and compared with traditional batteries, it has higher capacity, safety, lifespan and efficiency.
01It is used to improve the interfacial density between solid electrodes and electrolytes in solid-state batteries, and compared with traditional batteries, it has higher capacity, safety, lifespan and efficiency. -
 02Assist in the production of high-precision and high-strength parts, such as engine components and transmission systems.
02Assist in the production of high-precision and high-strength parts, such as engine components and transmission systems. -
 03Optimize the microstructure of hydrogen storage alloys to improve hydrogen storage capacity and hydrogen absorption/desorption cycle stability, and reduce the risk of hydrogen leakage.
03Optimize the microstructure of hydrogen storage alloys to improve hydrogen storage capacity and hydrogen absorption/desorption cycle stability, and reduce the risk of hydrogen leakage. -
 04Used to manufacture critical components that require high strength and durability, such as engine parts and aircraft structures.
04Used to manufacture critical components that require high strength and durability, such as engine parts and aircraft structures. -
 05Used in composite materials, for densification of rare metal powders to improve material strength and conductivity.
05Used in composite materials, for densification of rare metal powders to improve material strength and conductivity. -
 06Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), LTCC/HTCC packaging substrates, high-voltage electromagnetic insulators, etc., ensuring consistent electrical performance and dimensional accuracy.
06Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), LTCC/HTCC packaging substrates, high-voltage electromagnetic insulators, etc., ensuring consistent electrical performance and dimensional accuracy.